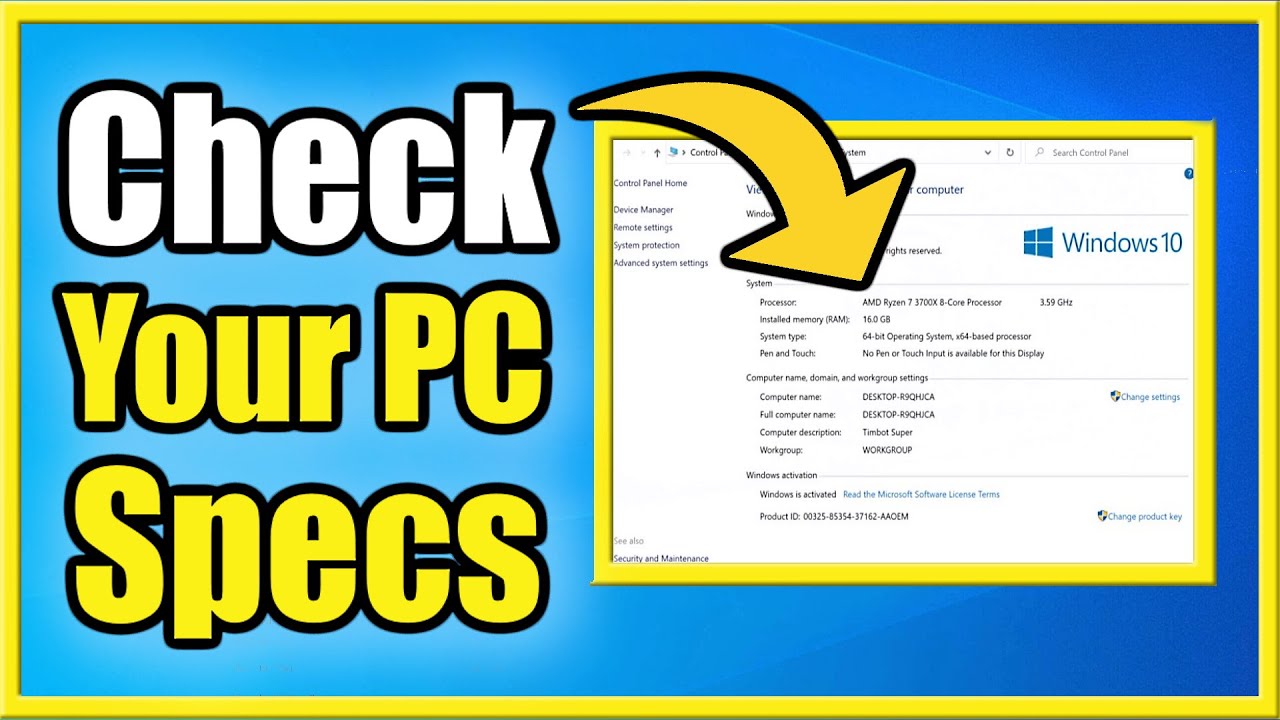
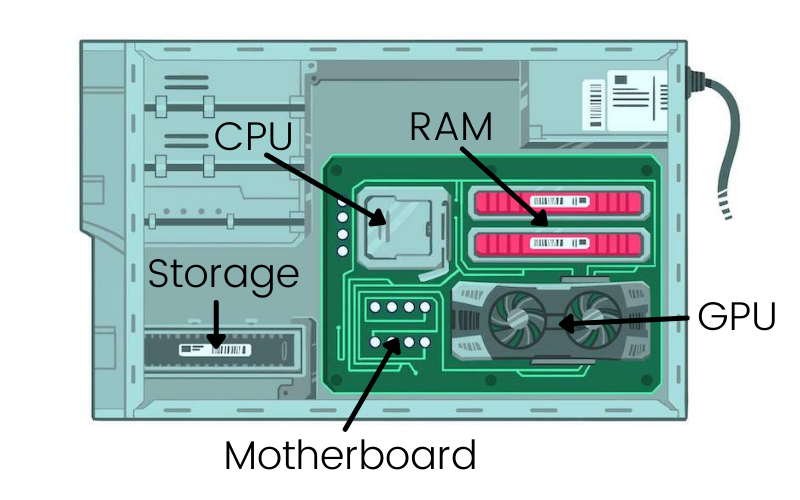
How to Check Your PC Specs in Windows 10
Checking your computer's specifications in Windows 10 in April 2025 is a straightforward process that provides valuable information about your system's hardware and software. By following these steps, you can easily access the details you need for various purposes.